Xinpeng WangI am a PhD student at the MaiNLP lab at LMU Munich . My supervisor is Prof. Barbara Plank . I'm currently a research scientist intern at Meta, and I was previously a visiting researcher at New York University advised by Prof. He He . Previously, I completed my M.Sc. degree in Robotics, Cognition, Intelligence at Technical University of Munich, where I was a student researcher at Visual Computing & AI Lab at TUM working on indoor scene synthesis. My research currently focuses on Alignment: Supervising the AI to do the right thing.
|

|
Selected ResearchThese include selected papers that represent my research, including some I currently want to highlight. |

|
Is It Thinking or Cheating? Detecting Implicit Reward Hacking by Measuring Reasoning EffortXinpeng Wang*, Nitish Joshi*, Barbara Plank, Rico Angell, He He preprint, 2025 arxiv / TRACE detects implicit reward hacking by measuring how quickly truncated reasoning suffices to obtain the reward, outperforming CoT monitoring and enabling hidden loopholes discovery. |
|
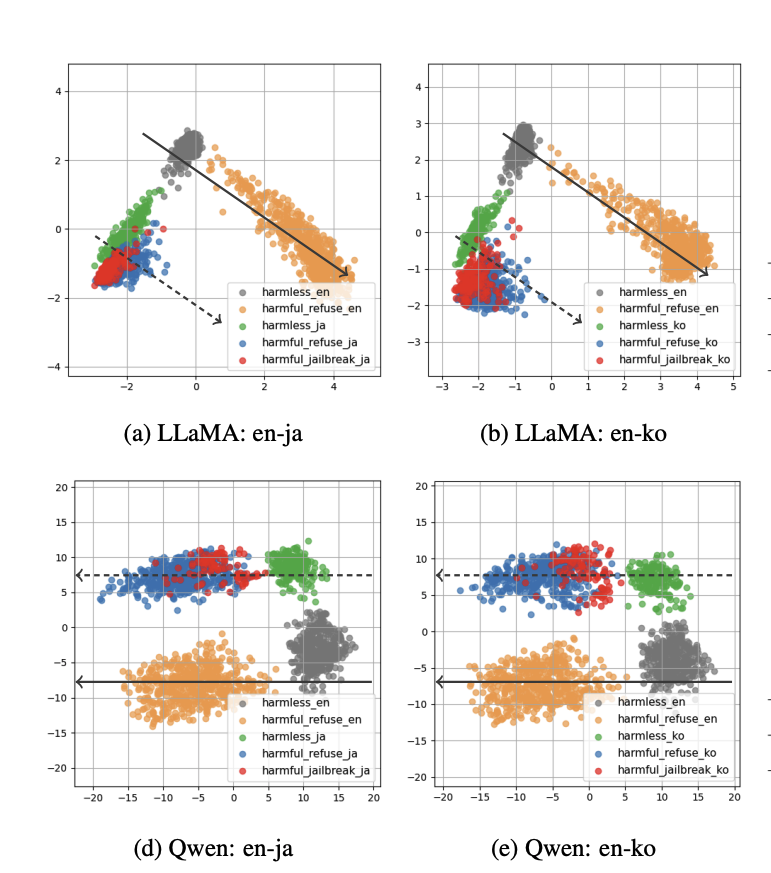
Refusal Direction is Universal Across Safety-Aligned LanguagesXinpeng Wang*, Mingyang Wang*, Yihong Liu*, Hinrich Schuetze, Barbara Plank NeurIPS, 2025 arxiv / Refusal directions in LLMs work across languages, revealing shared jailbreak mechanisms and raising the need for stronger multilingual safety. |

|
Surgical, Cheap, and Flexible: Mitigating False Refusal in Language Models via Single Vector AblationXinpeng Wang, Chengzhi Hu, Paul Röttger, Barbara Plank ICLR, 2025 arxiv / code / We propose a surgical and flexible approach to mitigate the false refusal in LLMs with minimal effect on performance and inference cost. |
|
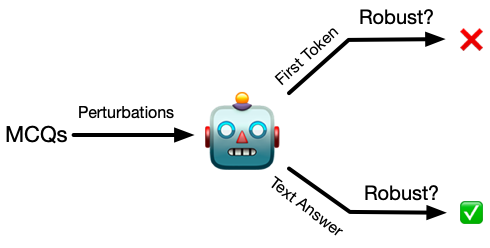
Look at the Text: Instruction-Tuned Language Models are More Robust Multiple Choice Selectors than You ThinkXinpeng Wang, Chengzhi Hu, Bolei Ma, Paul Röttger, Barbara Plank COLM, 2024 arxiv / code / We showed that text answers are more robust than first token answer in instruction-tuned language models, even debiased with SOTA first-token debiasing method. |
|
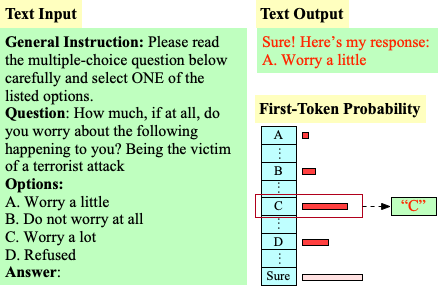
"My Answer is C": First-Token Probabilities Do Not Match Text Answers in Instruction-Tuned Language ModelsXinpeng Wang, Bolei Ma, Chengzhi Hu, Leon Weber-Genzel, Paul Röttger, Frauke Kreuter, Dirk Hovy, Barbara Plank ACL Findings, 2024 arxiv / code / We showed that the first-token probability evaluation does not match text answers in instruction-tuned language models. |
|
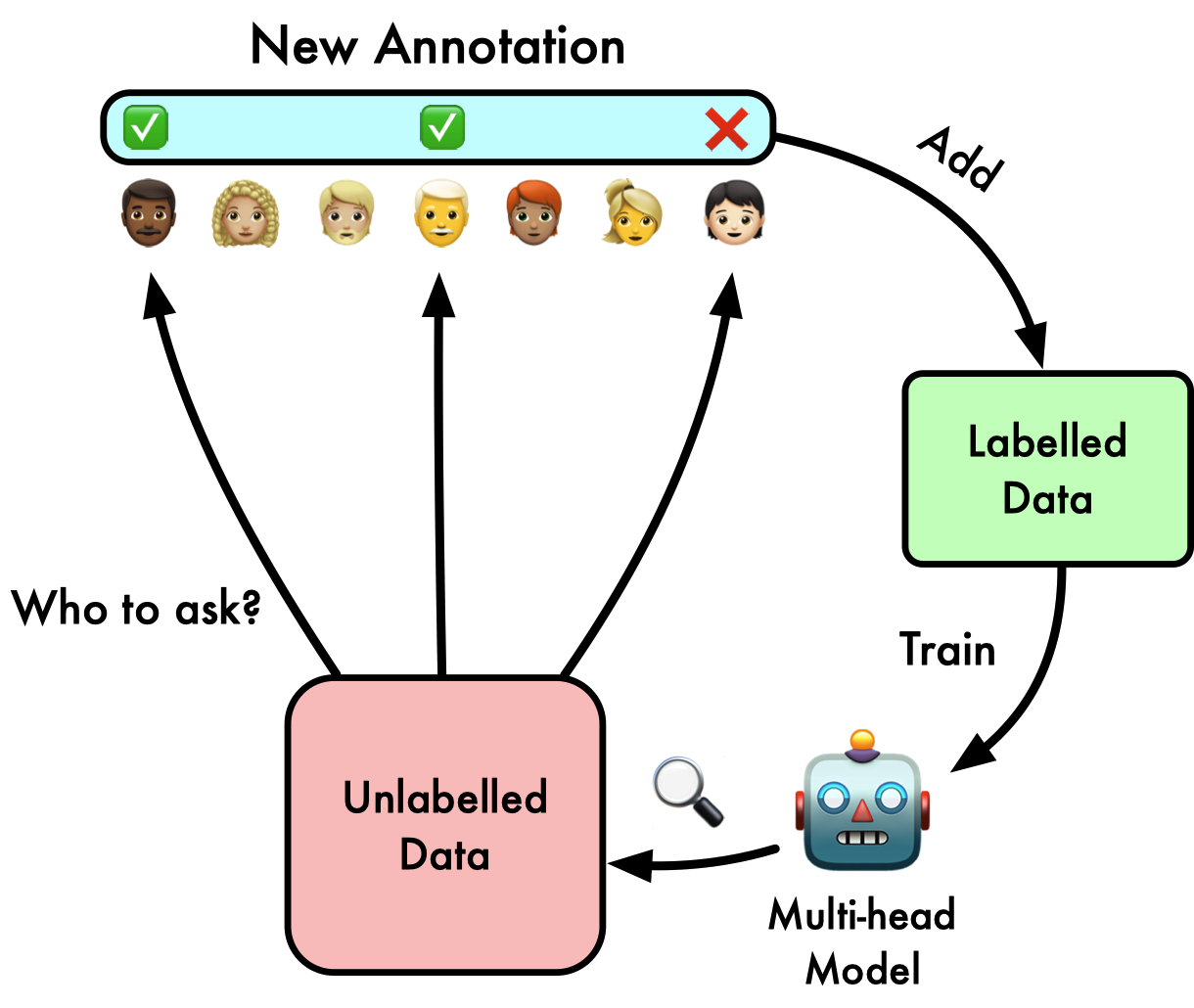
ACTOR: Active Learning with Annotator-specific Classification Heads to Embrace Human Label VariationXinpeng Wang, Barbara Plank EMNLP, 2023 arxiv / We proposed an active learning framework that utilizes a muli-head model to model individual annotators. We designed different acquisition functions and showed our active learning setup achieved performance comparable to full-scale training while saving up to 70% of the annotation budget. |
|
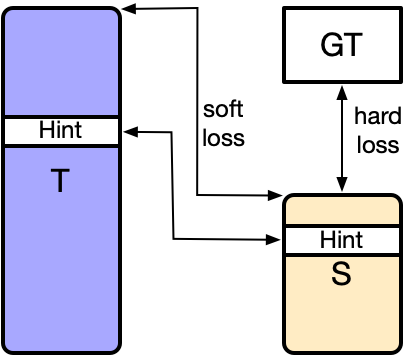
How to Distill your BERT: An Empirical Study on the Impact of Weight Initialisation and Distillation ObjectivesXinpeng Wang, Leonie Weissweiler, Hinrich Schütze, Barbara Plank ACL, 2023 arxiv / code / We showed that using lower teacher layers for pre-loading student model gives significant performance improvement compared to higher layers. We also studied the robustness of different distillation objectives under various initialisation choices. |
|
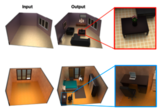
Sceneformer: Indoor Scene Generation with TransformersXinpeng Wang, Chandan Yeshwanth, Matthias Nießner 3DV, 2021 oral arxiv / video / code / We proposed a transformer model for scene generation conditioned on room layout and text description. |
Teaching |
|
Introduction to Deep Learning (IN2346)SS 2020, WS2020/2021 Teaching Assistant website / |
Student Supervision |
|
Sebastian Loftus - Improving LLM-Judgment for Diverging Human Preferences - Now at: PhD student at UCLouvain |
|
Shengyun Si - Navigating the Safety-Performance Trade-off in LLMs - Now at: PhD Student at TU Berlin XplaiNLP Group |
|
Chengzhi Martin Hu - Interpretability of Emergent Misalignment - Now at: PhD Student at TU Munich DAML Group |
|
Design and source code from Jon Barron's website |